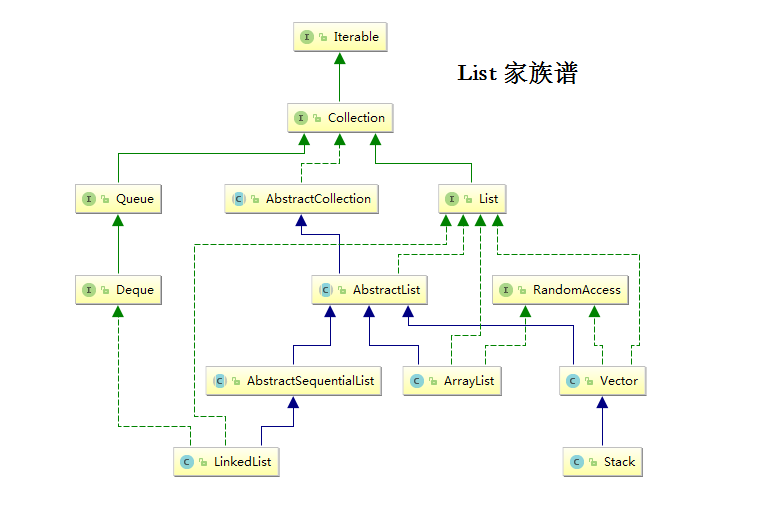
本文将通过 jdk 源码来看 List 的几种实现,以及这几种实现方式之间的区别。
注:本文基于jdk_1.8.0_144
源码看实现 ArrayList ArrayList 实际上就是个动态数组,相对 Arrays ,提供了对元素的多样化操作。
源码看构造 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class ArrayList <E> extends AbstractList <E> implements List <E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; transient Object[] elementData; private int size; }
单从基本结构来看,ArrayList 就是个动态数组,其内容实现为,用一个数组来存放数据,类型为 Object 。同时实现了四个接口,其中 RandomAccess 接口是个标记接口,表示元素可随机访问,在 Collections 类提供的集合操作方法中,有对此的特殊处理,包括查找算法与数据反转等。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public ArrayList (int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0 ) { this .elementData = new Object [initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0 ) { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity); } } public ArrayList () { this .elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } public ArrayList (Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0 ) { if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
ArrayList 提供了三个构造器,虽然大家常用的是无参数默认构造器,但是还是建议大家在初始化的时候,能使用指定容量的构造器。
添加元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public boolean add (E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); elementData[size++] = e; return true ; } public void add (int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1 , size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; }
在添加元素时,如果直接在尾部添加,效率方面还是没什么问题的,只需要进行扩容检查即可。 如果元素添加的位置不是尾部的话,就比较坑了,会调用 System.arraycopy 进行数据拷贝,效率还是比较低的。 在添加元素的时候,不会判断元素是否重复的,所以 ArrayList 允许重复元素。 添加元素在指定位置或者尾部,都会保证 ArrayList 的有序性。 在添加元素的时候,会进行容量检查,如果容量不足,会进行扩容,以保证容量足够承载所有元素,扩容实际还会调用 System.arraycopy 。扩容的内容会在下面讲到。 查找元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public E get (int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } E elementData (int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; }
由于实现方式是数组,查找数据的速度还是比较快,直接根据下标即可找到。
删除元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public E remove (int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; return oldValue; } public boolean remove (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null ) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } else { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } return false ; } private void fastRemove (int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; }
移除指定下标元素的时候,会进行数组拷贝重排,操作的数据是指定下标后面的数据 移除指定对象的时候,会分情况,如果对象为 null ,会进行判断,如果对象不为 null ,会调用 equals 方法判断,然后进行数据移除。 ArrayList 允许重复元素,在移除某对象的时候,会从前往后查找,找到后移除就结束了,并不会移除之后重复的元素。扩容 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 private void ensureCapacityInternal (int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity (int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow (int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1 ); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
ArrayList 在进行元素添加的时候,会进行容量检查。如果容量不足,会进行扩容,扩容后的大小为扩容之前的1.5倍。扩容后如果容量还不够,就会设置成所需的最小容量。同时容量最大有上限,为 Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 ,避免扩容后容量太大内存分配出现问题,同时也避免了有些虚拟机会占用数据一定长度的问题。
LinkedList LinkedList 是通过链表来实现 List 的,同时实现了 Deque 接口,使得 LinkedList 可做为双端队列和栈使用。
源码看构造 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class LinkedList <E> extends AbstractSequentialList <E> implements List <E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { transient int size = 0 ; transient Node<E> first; transient Node<E> last; private static class Node <E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this .item = element; this .next = next; this .prev = prev; } } }
可以看出,LinkedList 是通过链接来实现的。与 ArrayList 相比,多实现了一个 Deque 接口,实现了双端队列接口;少实现了一个 RandomAccess ,数据不可随机访问,需遍历查找。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public LinkedList () {} public LinkedList (Collection<? extends E> c) { this (); addAll(c); }
只有两个构造器,默认构造器不做任何操作,仅仅初始化一个空 List ;传入集合的构造器,会将集合内的元素,依次添加进链表。
添加元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public boolean add (E e) { linkLast(e); return true ; } public void add (int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } void linkLast (E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node <>(l, e, null ); last = newNode; if (l == null ) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } void linkBefore (E e, Node<E> succ) { final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node <>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null ) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
LinkedList 添加单个元素,不指定节点,则会将元素添加在链接尾部。指定节点,则会将元素添加在该节点前。不管哪种添加方式,所做的仅仅是改变下指针而已,不存在数据拷贝,高效。
移除元素同理,也是改变指针。但是由于链表不可随机访问,所以需要遍历链表来确定节点位置。
查找数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public E get (int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } Node<E> node (int index) { if (index < (size >> 1 )) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1 ; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } public E getFirst () { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null ) throw new NoSuchElementException (); return f.item; } public E getLast () { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null ) throw new NoSuchElementException (); return l.item; }
如果查找首尾节点,由于其实现保存了首尾节点信息,所以可以一步直接查找到。 如果查找指定索引,这里减少了查询群体,如果索引小于总数的一半,则只查询前一半,否则只查后一半,这样就少遍历了很多数据。 队列和栈 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public boolean offer (E e) { return add(e); } public E poll () { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null ) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } public void push (E e) { addFirst(e); } public E pop () { return removeFirst(); } public E peek () { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null ) ? null : f.item; }
LinkedList 同样提供了队列和栈相关的操作,使之可以被当作队列和栈使用。
Vector Vector 在实现方式和和 ArrayList 相似,都是使用数组来实现;不同的是 Vector 的方法基本都是同步的,线程安全,可在多线程情况下使用。同时,Vector 的扩容方式和 ArrayList 不同。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private void grow (int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0 ) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
可以看出,扩容的时候,主要看 capacityIncrement ,这个是在初始化的时候指定的扩容自动增长值。如果不显示指定的话,这个值默认为0。所以通常在不指定的情况下,扩容是按2倍扩容的。
Stack Stack 继承自 Vector ,提供了栈相关的操作,方法为同步方法,线程安全。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class Stack <E> extends Vector <E> { public Stack () { } public E push (E item) { addElement(item); return item; } public synchronized E pop () { E obj; int len = size(); obj = peek(); removeElementAt(len - 1 ); return obj; } public synchronized E peek () { int len = size(); if (len == 0 ) throw new EmptyStackException (); return elementAt(len - 1 ); } public synchronized int search (Object o) { int i = lastIndexOf(o); if (i >= 0 ) { return size() - i; } return -1 ; } }
Stack 以数组来实现栈,数组后面的元素作栈顶,出栈即为移除数组尾部元素,达到后进先出。
modCount是干什么用的 从本文最上面的图可以看出,ArrayList LinkedList Vector 全都继承自 AbstractList ,其中有个属性modCount 。List 相关操作,如果涉及到元素修改,都会触发 modCount++ 。
1 protected transient int modCount = 0 ;
下面我们来看看下面这段代码会输出什么:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("aa" ); list.add("bb" ); list.add("cc" ); list.add("dd" ); for (String s : list) { if ("bb" .equals(s)) { list.remove(s); } } System.out.println(list); }
我们预计会输出包含 aa, bb, cc 的值,但是实际呢?
Exception in thread “main” java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(ArrayList.java:901)
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(ArrayList.java:851)
没错,运行时抛了著名的 ConcurrentModificationException 异常,应该很多人遇到过。反编译下看下代码,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList (); list.add("aa" ); list.add("bb" ); list.add("cc" ); list.add("dd" ); Iterator var2 = list.iterator(); while (var2.hasNext()) { String s = (String)var2.next(); if ("bb" .equals(s)) { list.remove(s); } } System.out.println(list); }
实际 for(a:b) 只是个语法糖,用的还是迭代器。我们进入到迭代器,查看 next() 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 int expectedModCount = modCount;public E next () { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException (); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this .elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); cursor = i + 1 ; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } final void checkForComodification () { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException (); }
至此,就是大白的弟弟——真相大白了。在使用 Iterator 遍历的时候,会记录当时的 modCount ,赋值给 expectedModCount 。迭代器在每次调用 next() 方法取数据的时候,都会校验 modCount 是不是被修改了。如果被修改了,就会抛异常。
当然,如果正常使用 for 循环的话,是没有问题的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static void main (String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add("aa" ); list.add("bb" ); list.add("cc" ); list.add("dd" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { if ("bb" .equals(list.get(i))) { list.remove(i); } } System.out.println(list); }
输出结果如下:
[aa, cc, dd]
区别与联系 Stack 是 Vector 的子类。Stack 提供了 push pop peek search 操作栈的方法。Vector 和 Stack 线程安全,主要的操作数据方法均加了 synchronized 关键字;ArrayList 和 LinkedList 非线程安全。ArrayList 、 LinkedList 、Stack 实现方式为数组,LinkedList 实现方式为双向链表。效率方面,数组实现的三个类,随机查找数据效率高,增删非最后一个数据效率低;链表实现的 LinkedList 查询数据效率低,但是对于频繁的增删数据有极大的优势。 扩容方式不同。ArrayList 是扩容1.5倍,Vector 如果不指定每次扩容大小,或者指定大小小于等于0,则在扩容时扩容2倍。 总结 List 是有序集合,子类数组有序。ArrayList 是大小可变的动态数组,可重复、可为 null ,查询数据迅速,非尾部追加数据消耗大,非线程安全。LinkedList 是双向链接实现,可重复、可为 null ,查询效率低,增删效率高,非线程安全,可作双端队列及栈使用。Vector 的实现方式也是数组,与 ArrayList 的最大不同就是,大部分 public 方法是同步的,线程安全。Stack 是 Vector 的子类,额外增加了操作栈的相关方法。使用迭代器(包括 for(a:b) )的时候,在循环内部不可以用 remove 方法,否则会报 ConcurrentModificationException 异常,因为迭代器在 next 的时候,会检查 modCount 。